Databricks Unity Catalog: A Practitioner's Guide to Secure, Scalable Data Governance
Centralize governance across your Databricks workspaces with streamlined metadata, access, and lineage management—built to scale securely across clouds.
Databricks is a unified analytics platform for building, deploying, and maintaining enterprise-grade data solutions at scale. It leverages Apache Spark, Delta Lake, and MLflow to provide data engineering, analytics, and machine learning capabilities. In this blog, we explore a called Unity Catalog.
Why Use Databricks Unity Catalog?
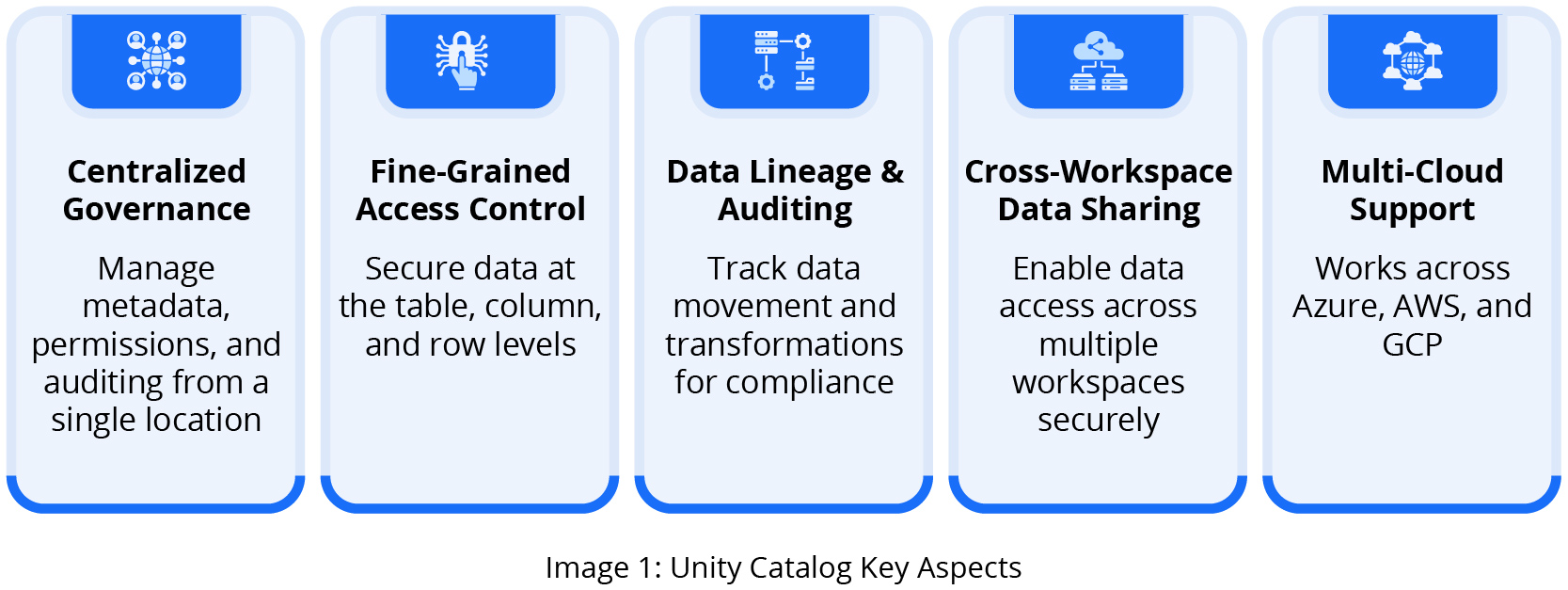
Databricks Unity Catalog provides centralized access control, auditing, lineage, and data discovery capabilities across Databricks workspaces. It simplifies security, access control, and metadata management while enabling efficient governance across all data assets.
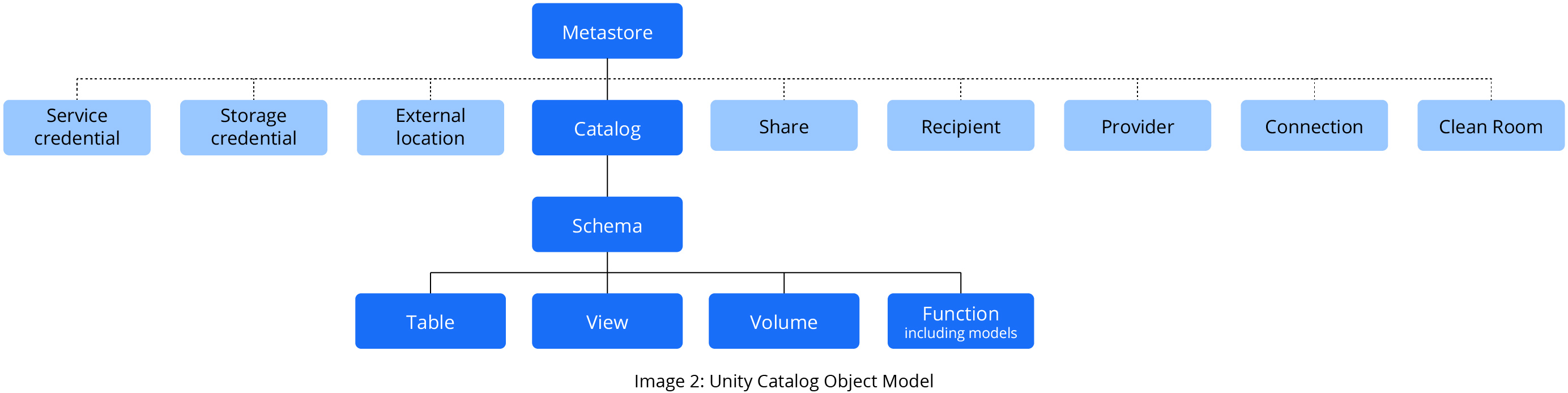
Unity Catalog Hierarchy
The hierarchy of primary data objects in Unity Catalog follows a structured flow from Metastore to Table or Volume:
- Metastore: The top-level container for metadata. Each metastore exposes a three-level namespace (schema.table) that organizes data.
- Catalog: The first layer of the object hierarchy is used to organize data assets.
- Schema: Also known as databases, schemas are the second layer of the object hierarchy and contain tables and views.
- Volume: Volumes are the lowest level of the object hierarchy, alongside tables and views, and provide governance for non-tabular data.
- Table: Tables and views are at the lowest level in the object hierarchy.
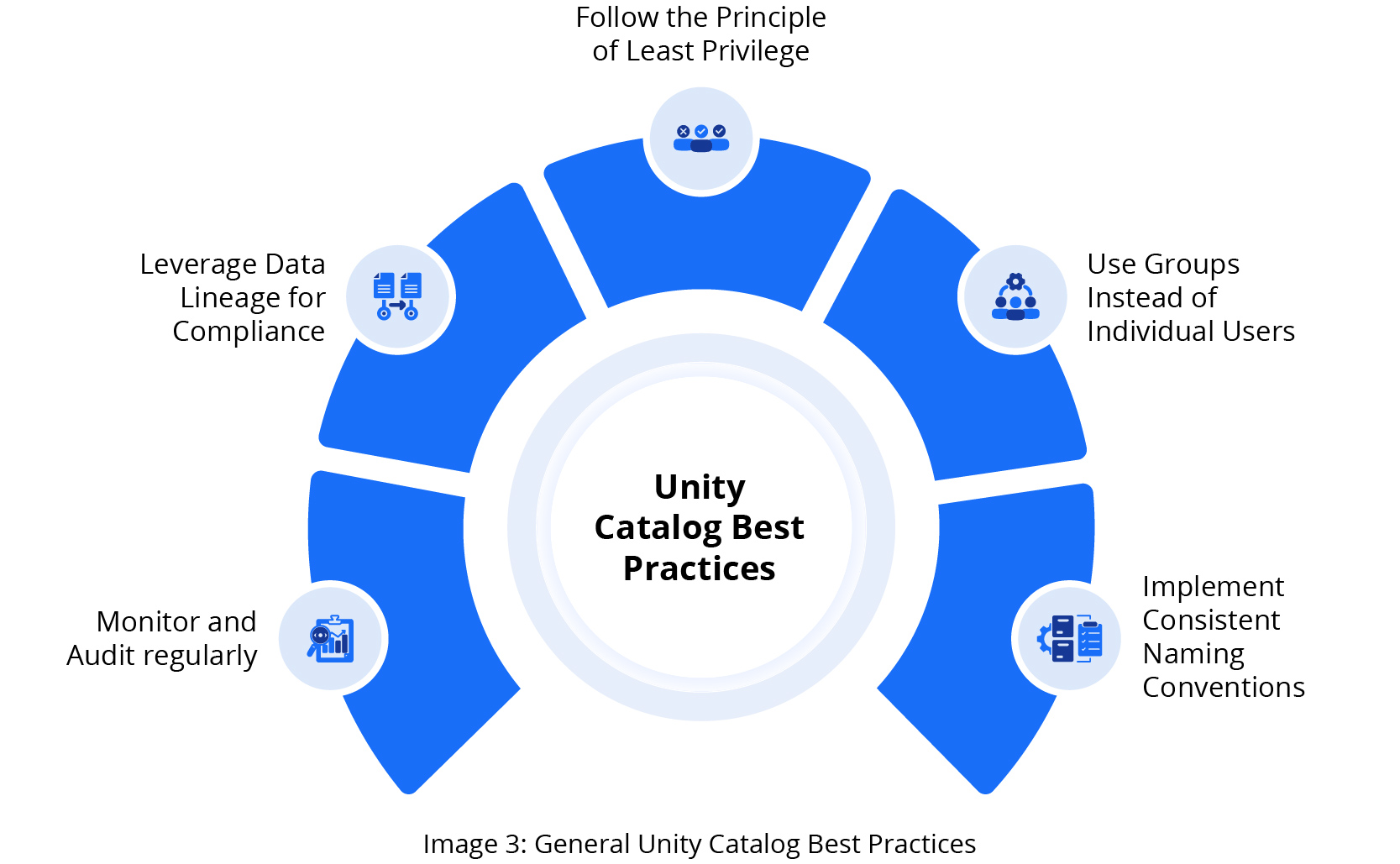
Catalog Best Practices
For effective governance and organization, it is recommended to create the three catalogs described next.
Development Catalog
The Development Catalog is designed to facilitate the creation of data pipelines. Users can read from production tables (published and non_published) within Access Control Lists (ACLs) and write to their schema in this catalog. Upon onboarding, a default schema named team is created in the development catalog. Additional schemas can be made by following the steps outlined in the Define Schemas section.
Non_Published_* Catalog
The Non_Published Catalog is considered part of the production environment. Its schemas maintain raw, curated, and consumption datasets, serving as a crucial intermediary step in data management.
Published_* Catalog
The Published Catalog exclusively contains views exposed to data analysts and consumers. This catalog is the final presentation layer for processed and refined data, ensuring end-users access the most relevant and reliable information.
Other Best Practices
Following the suggestions in Image 3, your organization can effectively implement Unity Catalog, creating a secure, well-organized, and compliant data management environment that supports your business objectives while maintaining strict control over data access and usage.
Service Principals
Service principals are essential components for automation in data management workflows. These entities are designed to facilitate secure access for CI/CD pipelines and job execution, enabling seamless integration of automated processes within the Databricks ecosystem. Organizations can maintain robust security measures by utilizing service principals while streamlining their data operations.
Service Principals in Unity Catalog provide a powerful mechanism for role-based access management in automated workflows. This approach ensures that each automated process or integration has precisely the level of access it requires, no more and no less. By implementing service principals, companies can significantly enhance their data governance practices, reducing the risk of unauthorized access while promoting efficient and secure data handling across their entire data infrastructure.
Use Cases: Secure Data Sharing with Delta Sharing
Delta sharing in Unity Catalog enables secure data sharing with external partners, vendors, and data consumers without data duplication.
Benefits of Delta Sharing:
- Share data securely without replication
- Supports cross-cloud sharing across AWS, Azure and GCP
- Fine grained access control at the row and column level
- Avoids redundant raw, curated, and egress layers, reducing processing and storage costs
Steps to Implement Delta Sharing:
- Enable Delta Sharing in Unity Catalog
- Create a share and add the required tables/views
- Grant access to external users (e.g., an O9 analyst team)
- Monitor and Audit Data Access through Unity Catalog logs
Data Lineage: Tracking Data Transformations
Data lineage helps organizations track how data flows from raw ingestion (source) to upstream (report) tables and deduplication of processing, reducing costs.
Step-by-Step Implementation for Unity Catalog Integration
Unity Catalog implementation involves setting up a metastore, configuring storage access, defining external data sources, organizing catalogs and schemas, creating tables, implementing security measures, enabling data lineage tracking, and managing access privileges. This process establishes a secure, well-organized data management environment that supports business objectives while maintaining strict control over data access and usage.
- Establish the Unity Catalog Metastore
Access the Databricks Admin Console to set up the Unity Catalog Metastore. This crucial step involves creating the metastore, assigning administrative roles to key personnel, and connecting it to your organization's cloud storage infrastructure. This foundation ensures proper data governance and access control. - Set Up Storage Access
Implement storage credentials within Databricks to manage secure access to your data. This process includes configuring the necessary identity and access management roles, ensuring only authorized personnel can interact with sensitive data. Verify the setup to confirm seamless connectivity between Databricks and your storage solutions. - Define External Data Sources
Register external locations to enable access to data stored outside of Databricks. This step is vital for integrating diverse data sources into your unified data management strategy. Implement appropriate permission structures to maintain data security while allowing necessary access. - Organize Data Catalogs
Create a structured hierarchy of data catalogs to manage your organization's data assets efficiently. Establish separate catalogs for development, non-published data, and published data. This organization facilitates better data discovery, governance, and lifecycle management. - Establish Data Schemas
Within each catalog, define schemas to categorize and organize your data further. Implement access controls at the schema level to ensure that different teams, such as analysts, access relevant data sets appropriately. - Create Data Tables
Set up managed and external tables to store and access your data effectively. Databricks controls managed tables, while external tables allow you to connect to your cloud storage data. This flexibility balances performance, cost, and data ownership requirements. - Implement Advanced Security Measures
Implement column-level and row-level security to enhance data protection. These features allow you to control access to specific data elements based on user roles or other criteria, ensuring that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized personnel. - Enable Data Lineage Tracking
Utilize Unity Catalog's built-in data lineage tracking capabilities. This feature automatically records the data flow through your systems, providing valuable insights for compliance, troubleshooting, and data quality management. - Manage Access Privileges and Auditing
Implement a robust system of access controls using granular permissions. Regularly audit access logs to monitor data usage, detect potential security issues, and ensure compliance with data governance policies.
Conclusion
Implementing Databricks Unity Catalog enhances data governance, security, and accessibility. Following this guide, practitioners can seamlessly integrate Unity Catalog into their Databricks environment, ensuring efficient and secure data management.



